Mri scan of head in sagittal plane.
Floor of fourth ventricle ppt.
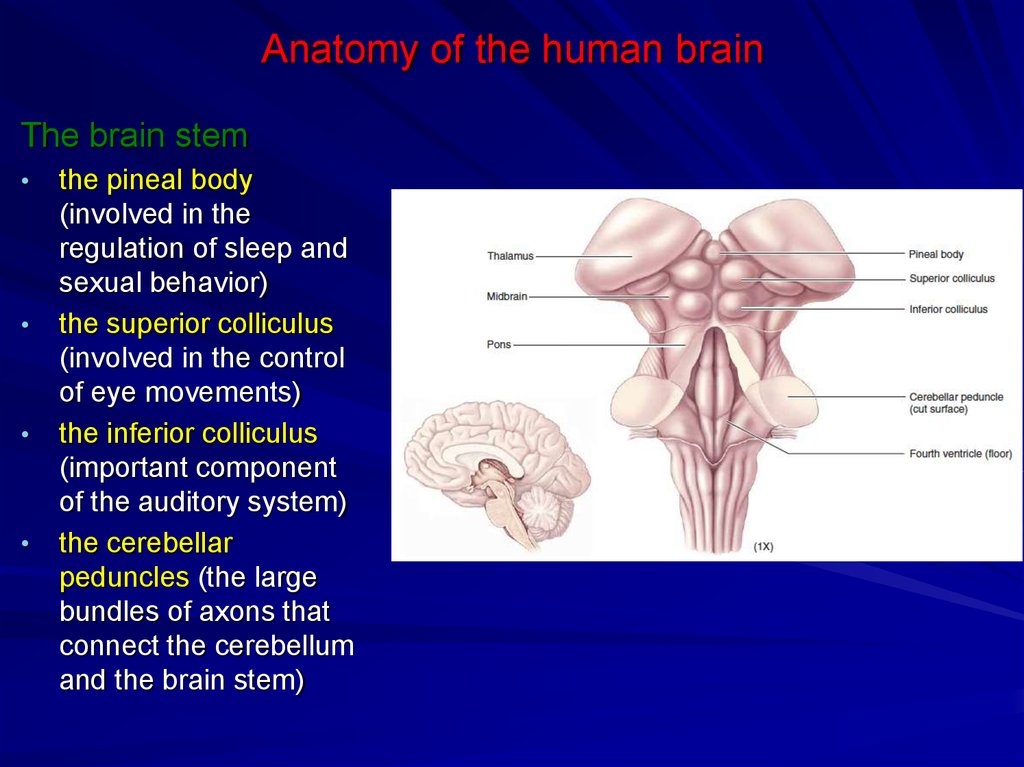
The fourth ventricle has a roof at its upper posterior surface and a floor at its lower anterior surface and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side.
Central spinal canal bathes the spinal cord.
3 the fourth ventricle is situated dorsal to the pons and upper part of medulla oblongata and ventral to the cerebellum.
4 1 lateral walls of fourth ventricle.
The border between the pons and medulla occurs approximately at the level of the foramina of luschka.
It has a diamond shape and is located in the upper portion of the medulla.
4 what are the boundaries of fourth ventricle.
The glistening white floor of the fourth ventricle is the posterior surface of the brain stem.
The caudal tip of the fourth ventricle where it becomes the central canal is known as the obex.
Projection of the ventricles onto the left surface of the brain.
The two taenia meet at the inferior angle of the ventricle to form a small fold called obex.
Eor and outcomes were satisfactory in 90 of patients including those harboring large tumors or lesions attached to the lateral or superolateral recesses of the ventricle.
The inferolateral margins marked by a narrow white ridge called taenia.
Csf produced and or flowing into the fourth ventricle can exit to the subarachnoid space through lateral apertures and a single median aperture located in the inferiorportion of the roof.
The features of the lower part of the floor of fourth ventricle resemble with that of a pen nib hence it is called calamus scriptorius 17.
Fourth ventricle central canal fourth ventricle mesencephalic aqueduct third ventricle position situated ventral to cerebellum and dorsal to pons and cranial half of medulla 5.
Features of the floor of the fourth ventricle rhomboid fossa the floor of the 4th ventricle displays the following features.
From the 4th ventricle the fluid drains into two places.
4 2 floor or ventral wall of fourth ventricle 4 3 roof of the fourth ventricle.
The fourth ventricle is the last in the system it receives csf from the third ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct.
The superior pontine part of the floor begins at the aqueduct and expands to the lower margin of the cerebellar peduncles.
Specifically it spans from the obex an area in the medulla.
The fourth ventricle has an anterior ventral floor with a characteristic diamond shape named the rhomboid fossa and a posterior dorsal tent shaped roof.
It lies within the brainstem at the junction between the pons and medulla oblongata.
The whole floor is split into left and right symmetrical halves by a median sulcus which stretches from the aperture of the aqueduct of the midbrain above to the commencement of the central canal below.
Exposure of the fourth ventricle was satisfactory in all of the patients and the floor of the fourth ventricle could be visualized early and be protected.